Research Notes
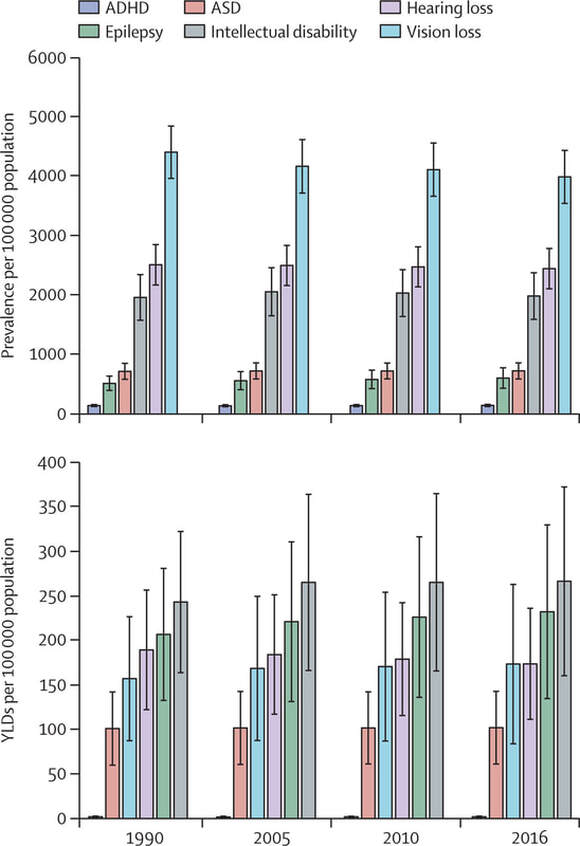
From inception, GRDDC recognised the challenges presented by various debates on terminologies for children with developmental disabilities in different cultural contexts. There is also a lack of consensus in the literature on which health condition or disorder constitutes a developmental disability. We recognise that diverse conditions and disorders may impair the development of children in early childhood. Guided by the United Nations' Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, we consider children under 5 years with developmental disabilities as children under 5 years who have long-term physical, visual, hearing and communication, learning (cognitive and intellectual) and psychosocial/behavioural impairments which, in interaction with various barriers, may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with other children. While we are committed to serving all children with disabilities and their families, we are constrained to align our target conditions and terminologies with those derived from ICD Codes and other Classification Systems for which there is an existing infrastructure for estimating the burden of disease in line with international practice. As a result, GRDDC has chosen to focus on the following conditions for which global estimates are periodically reported by the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), a global leader in population health metrics.
This approach allows us to link mortality, disabilities and other health outcomes among children under-5 years in a manner that will optimise our advocacy engagements with policy makers in global health. This list will be updated in our future data analysis as more global, regional and national estimates for all the 194 countries included in the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study become available. We also hold the view that "a rising tide lifts all boats!
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral Palsy
- Epilepsy
- Hearing Impairment
- Developmental Intellectual Disability
- Vision Impairment
- Congenital Birth Defects (including Neural Tube Defects and Down Syndrome)
This approach allows us to link mortality, disabilities and other health outcomes among children under-5 years in a manner that will optimise our advocacy engagements with policy makers in global health. This list will be updated in our future data analysis as more global, regional and national estimates for all the 194 countries included in the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study become available. We also hold the view that "a rising tide lifts all boats!